
Climate control is an important aspect of every home. It helps to regulate the temperature and keep you comfortable no matter what the weather is like outside. In this blog post, we will give a climate control definition and discuss how to use it in your home. Stay warm in the winter and cool in the summer with climate control!
What is climate control?
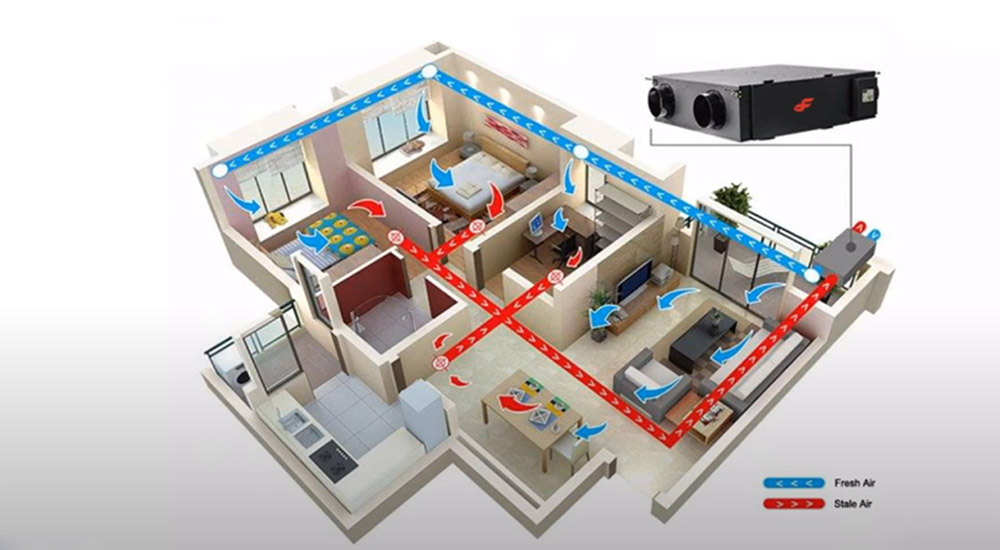

Climate control refers to the regulation of temperature and humidity in an enclosed space such as a home or office. Climate control systems use thermostats, fans, vents, and other devices to keep these variables under close watch so that people can live comfortably year-round regardless of what’s happening outside their windows!
There are a few different types of climate control systems available on the market today. The most common type is the central heating and cooling system, which distributes the conditioned air through ducts throughout your house. If you don’t have a central HVAC system, you may have a window unit or portable AC unit instead.
No matter what type of climate control system you have in your home, it’s important to understand how to use it properly!
Climate Control Capabilities

So, what is climate control? In short, it’s the regulation of temperature and humidity in an enclosed space. The climate control system allows you to regulate the temperature and humidity in your home.
Climate control is especially important in climates where the weather can be extreme. In cold winters for example climate control helps you stay warm and cozy; while the air conditioning keeps it cool on those sweltering summer days with an AC unit or fan.
Climate Control has other capabilities besides just regulating temperature and humidity levels inside of buildings. It also gives users access to some pretty amazing features like:
- Programmable Thermostats
- Smart Sensors for The Blind And Deaf
- Voice Control (Alexa) Integration with Smart Home Devices Like Lights Or Door Locks
With voice control capabilities and the ability to connect with other smart devices, climate control can make your life a whole lot easier!
Air temperature

Air temperature is the most important climate control variable to regulate in your home. The ideal air temperature for most people is around 70 degrees Fahrenheit, but this can vary depending on personal preferences. You may want to adjust the thermostat up or down a few degrees to find the perfect comfort level for you and your family.
It’s important to note that air temperature is not the same thing as surface temperature, so you can’t just walk around with a thermometer in hand trying to figure out what it feels like inside your house!
Humidity level

The humidity level is another important climate control variable to consider. The ideal humidity level for most people is around 50%, but this can vary depending on your personal preferences and the type of climate you live in.
Humidity levels that are too high or too low can cause discomfort, so it’s important to keep an eye on this variable and adjust it as needed.
You can use a hygrometer to measure the humidity level in your home, or you can use the “humidistat” setting on your thermostat to automatically adjust it as needed.
If you find that the humidity level in your home is regularly outside of your comfort zone, there are a few things you can do to adjust it. First, make sure that your HVAC system is the right size for your home so it’s not too big or small. You can also install a humidifier (or dehumidifier) to help regulate humidity levels throughout the year without having to adjust them manually every time they get out of whack!
Air ozonization

Air ozonization is the process of creating ozone from an electric current. Ozone can be used as a disinfectant in air purification systems because it kills bacteria and viruses on contact without harming human tissue or other living things.
Air purification with ozone has been shown to have health benefits such as reducing allergies and asthma symptoms for some people who suffer from these conditions regularly when not exposed to clean air sources like outdoors where pollution levels are typically very low compared indoors.
Air ionization

Air ionization is the process of creating ions from an electric current. Ions are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained one or more electrons and can be positively or negatively charged.
Positively charged ions are often called “anions”, and negatively charged ions are often called “cations”. The presence of positive and negative ions in the air has been shown to have health.
There are a few ways to introduce positive and negative ions into the air in your home, but one of the most popular methods is to use an air ionizer.
An air ionizer is a device that generates ions and distributes them into the air. You can buy an air ionizer for your home, or you can install one in your HVAC system!
How does the climate control system work?

A climate control system is used to regulate the temperature and humidity inside a building. It may also be known as an HVAC system because it does this through heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), and sometimes even humidification of spaces within your home!
The Climate Control System’s main function is to provide comfortable conditions for people who live thereby keeping them warm during cold weather periods and cool when temperatures rise too high outside.
The climate control system works by first heating up or cooling down the incoming air depending on the room’s desired temperature set by you, the homeowner! Once this air has been adjusted to your liking, a blower will push it throughout all of the rooms in your house using ductwork until it reaches each vent. From there, it’s up to Room Temperature Sensors (RTS) which monitor each room’s climate and adjust accordingly.
Basic heating and cooling technologies
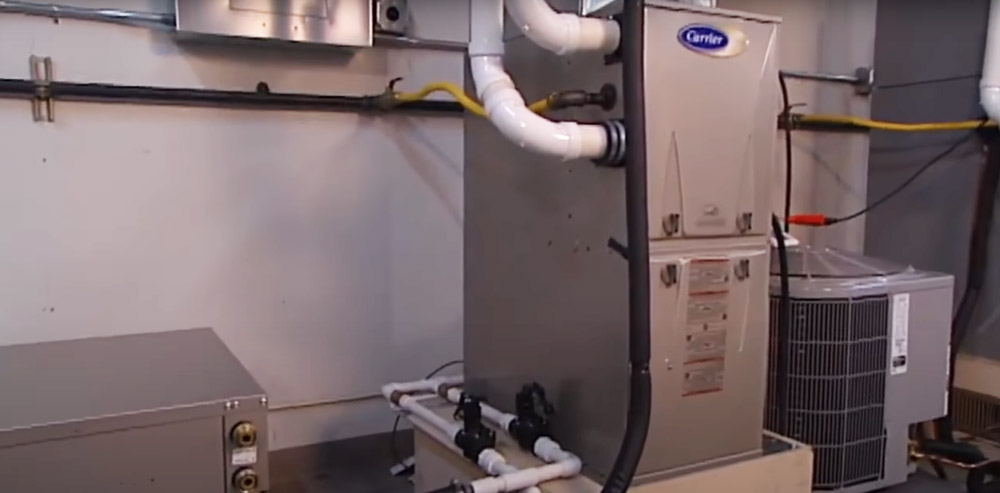

Central heating and cooling technologies use a variety of different fuels to heat or cool the air indoors. The most common fuel used is electricity, followed by natural gas and propane.
Heating:
The three basic types of central heating systems are forced air, hot water, and steam. In a forced-air system, heated air is circulated through ducts to registers in each room. A hot water system uses pipes that run from the furnace or boiler to radiators throughout the house.
Steam systems also use pipes to distribute steam but it goes directly into rooms instead of being stored in radiators first.
Cooling:
There are two main types of central air conditioning systems – refrigerant and absorption. Refrigerant systems are more common because they use less energy than absorption systems.
They work by circulating refrigerant through the coils on a fan coil unit (FCU) which cools down incoming air from outside before pushing it into rooms where RTS sensors adjust room temperatures depending on what you’ve set them at!
Insulation, materials, and passive design

Materials used in the construction of a building can play an important role in how energy is transferred both indoors and outdoors. The three main types of insulation are fiberglass, cellulose, and foam.
- Fiberglass is made up of tiny glass fibers that trap air and prevent it from moving through walls, ceilings, or floors.
- Cellulose is made from recycled paper products such as newspapers or cardboard boxes.
- Foam insulation comes in two forms – spray foam and rigid foam. Spray foam is applied wet and then dries to form a thick layer of insulation. Rigid foam boards are installed between wall studs or rafters before the drywall goes on.
Windows and doors also play a role in how energy moves in and out of a building. Windows that are Energy Star certified have a low U-Factor which means they allow less heat to escape in the winter and less cold air to enter during the summer. Doors should have an R-Value of at least 13 to prevent warm air from escaping in the winter and cool air from entering in the summer.

Passive design is a strategy that can be used in both new construction and existing buildings to reduce energy use without using any special equipment or technology. Some common features of the passive design include orientation to take advantage of sunlight, shading devices to control incoming light and heat, use of natural ventilation, and thermal mass materials that store energy from the sun or indoor activities such as cooking.
Air quality and ventilation
Air quality is a growing concern for many Americans who live in cities or other areas with poor air pollution levels.

Ventilation systems are an excellent way to filter out pollutants from the air you breathe, but they can also be expensive and require regular maintenance by professionals such as HVAC technicians.
Poorly maintained ventilation systems may not work properly which means they won’t remove contaminants like dust mites or pet dander that cause allergies.
Indoor air pollutants include mold spores, dust particles, bacteria, viruses, and allergens such as animal dander or pollen grains that can trigger asthma attacks if inhaled into lungs where they irritate sensitive tissue lining of respiratory passages leading towards bronchial tubes (which carry oxygenated blood away).
Poor ventilation in buildings can also lead to poor quality control over moisture levels which increases the risk for the growth of mold spores on surfaces like drywall panels or wood floors.
Good ventilation systems use exhaust fans that pull stale air out from inside your home and replace it with fresh air coming through windows or doors so there is less pressure build-up inside when cooking meals during cold weather season months where we tend to stay indoors more often than usual due to shorter daylight hours outside!
Management System Composition
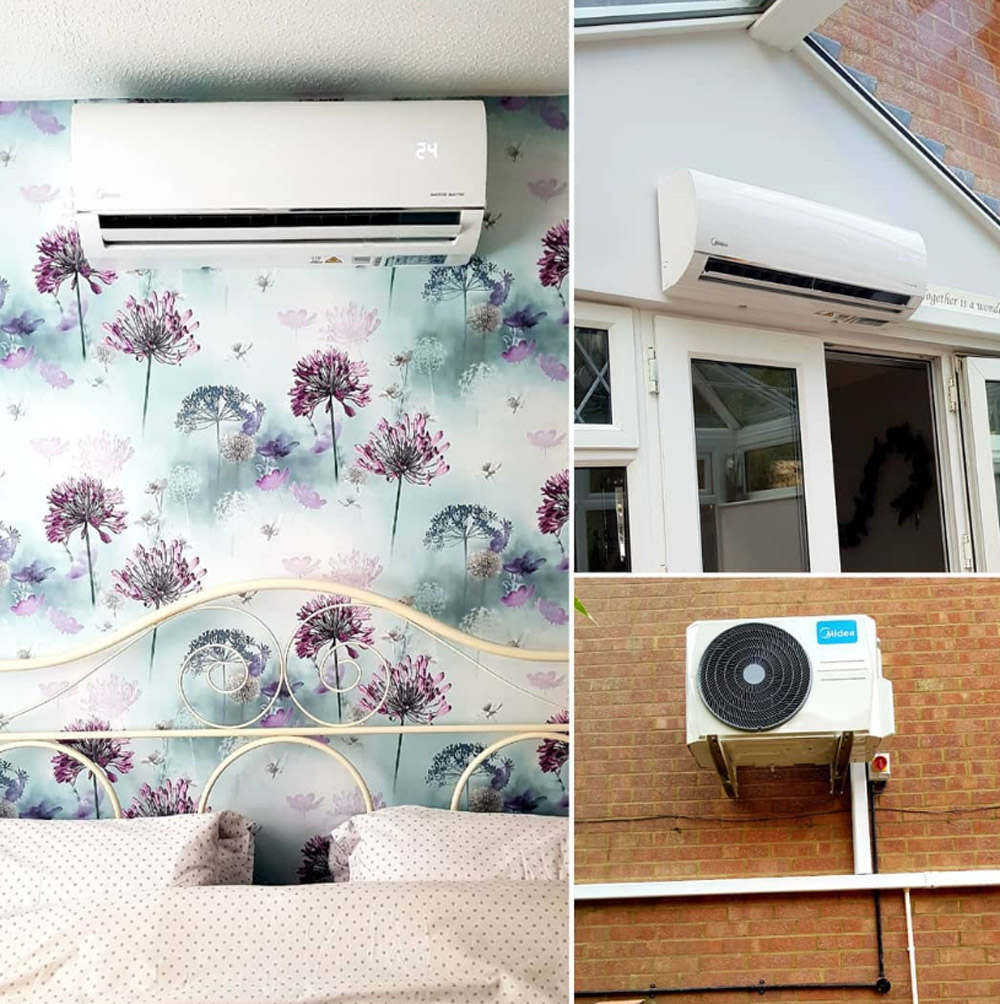

The device consists of four key components:
- Heating equipment that will produce heat energy from either natural gas or electricity; these devices are called furnaces in North America but boilers elsewhere around the world due to their purpose being solely focused on providing warmth rather than air conditioning as well.
- Air conditioners that cool down warm air by using refrigerants and other chemicals inside coils to remove moisture from inside rooms through evaporation processes; these devices are typically only found in warmer regions because they require very little maintenance compared with heating systems which can break down easily due to their age or wear out over time due to its reliance on electricity (which may not always be available during power cuts).
- Humidifiers that add moisture into dry spaces so people feel more comfortable when it’s hot outside of their homes; these devices come in different sizes depending on room size and types such as small desk-top models meant for personal use while larger units designed specifically for whole houses exist too. Some humidifiers also can reduce humidity levels if they get too high indoors.
- Ventilation systems that remove stale, old air from inside a building and replace it with fresh outdoor air; these devices can be either powered by electricity or mechanically through fans which create negative pressure within the home so outside air is pulled inwards instead of dirty air being pushed out.
The climate control management system in your home is responsible for regulating two things – temperature and humidity. The thermostat measures the ambient temperature in your home and sends a signal to the air handler telling it how much heat needs to be added or removed from the air to maintain your desired temperature.

The humidity sensor on the thermostat measures how much water vapor is present in the air and sends a signal to the air handler telling it how much moisture needs to be added or removed from the air to maintain your desired humidity level.
Most modern climate control management systems come with a built-in dehumidifier that can be turned on when the humidity level gets too high. This is a great feature to have because it will help to reduce the amount of moisture in the air which will prevent mold spores from growing and spreading.
How I to improve climate control management system

If you’re not happy with the climate control management system in your home, there are a few things you can do to improve it:
- Replace your old thermostat with a new programmable model that has a built-in humidity sensor
- Install a whole-house dehumidifier to reduce the amount of moisture in the air
- Upgrade your air handler or condenser unit to one that’s more energy efficient
- Clean or replace your filters regularly to ensure good airflow through the system
- Close off unused rooms and vents to prevent the air from becoming too warm or too dry
- Insulate your home properly to help keep the temperature and humidity consistent indoors
These are just a few tips to get you started. If you’re still not happy with the climate control management system in your home, contact a professional HVAC contractor for advice. They’ll be able to recommend specific solutions that are tailored to your needs and budget.
Pros and cons of climate control

The pros of climate control are that it can improve air quality and reduce allergens in your home. This is especially important if you’re someone who suffers from asthma or other respiratory illnesses because having clean air circulating throughout the house will help to prevent flare-ups. It’s also good for people with allergies because mold spores are less likely to grow on surfaces like furniture when there isn’t any moisture present; this means no more sneezing fits due to dust mites!
In addition, temperature fluctuations between rooms won’t be an issue anymore since they’ll always stay comfortable regardless of where they go inside their own homes thanks to these systems installed by experts at HVAC companies near you today
Some possible cons might be that some people have trouble adjusting to the new temperature and humidity levels in their homes after installing climate control management systems. There might also be concerns over whether or not these types of systems are safe for children because they could potentially get into trouble by messing with buttons and switching on them accidentally due to curiosity.
77-1 – trouble adjusting to the new temperature and humidity levels in their homes
Another downside is that this type of system requires professional installation which can be costly depending on the size of your home as well as other factors such as how many rooms need work done
The cost will vary between companies based on labor hours required (which is usually around two-three) but most experts estimate that it’s somewhere between $1500 – 3000 dollars’ total including all materials needed like ducts wires thermostats etcetera; however, prices may vary
System recommendations

There are a lot of different climate control management systems on the market these days, so it can be tough to decide which one is right for your home. If you’re not sure where to start, here are a few suggestions:
- If you want a system that’s easy to use and doesn’t require any programming, then a basic programmable thermostat is a good option. These thermostats allow you to set the temperature manually or program them to turn on and off at certain times of the day. They also come with humidity sensors so you can keep track of the moisture levels in your home.
- If you’re looking for something more advanced, there are options like smart thermostats that can be controlled remotely using a smartphone or tablet. These thermostats can also learn your habits and preferences over time, so they can adjust the temperature and humidity automatically to match your needs.
- If you’re looking for a system that will take care of everything for you, then a whole-house dehumidifier might be the best option. Dehumidifiers remove moisture from the air, which helps to reduce allergens and improve air quality. They also work well in conjunction with other climate control management systems, like air conditioners and heaters, to help keep the temperature and humidity consistent throughout your home.
No matter what type of system you choose, make sure to consult with a professional HVAC contractor to get the best results. They’ll be able to recommend specific solutions that are tailored to your needs and budget.
How do you install climate control?
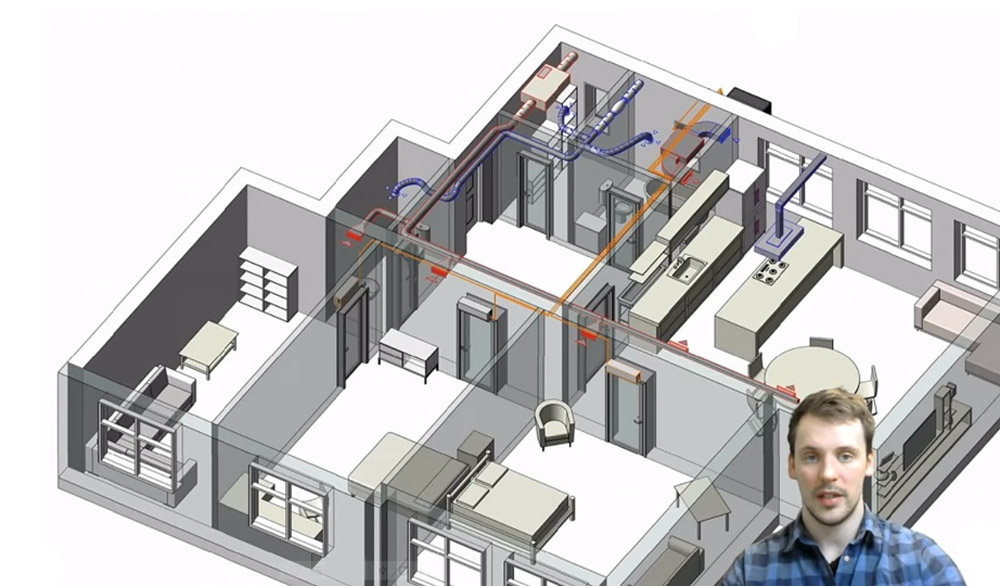
There are many different options available that can be installed by professionals or DIY (Do It Yourself). You’ll need some basic tools like screwdrivers and pliers as well as an understanding of electrical wiring before starting this project; however, if it’s too difficult don’t worry because most people find success on their first attempt with proper guidance!
The best way to get started is by measuring out where everything will go so there won’t be any surprises when installing your new system. Next, take note of which rooms need heating/cooling more than others due to high traffic areas such as kitchens living rooms etcetera.
All these points should be marked clearly on paper with measurements taken from floor plan drawings or photographs (if available).
Once all this information has been gathered it’s time for installation day! Make sure you have everything ready before starting so there won’t be any delays; for example: make sure your ductwork is clear of debris and obstructions, check if the power supply box has an outlet nearby where a temporary extension cord can reach into the area that needs work done.
After installing climate control management systems, homeowners will notice changes in their energy bills over time because they’re no longer wasting money heating rooms that don’t need it as well as saving electricity costs due to lower cooling requirements during summer months when temperatures are higher outside than inside homes.
Is Climate Control Better than AC?

The answer is yes! Climate control has many benefits for homeowners who are looking to save money on their energy bills as well as reduce carbon emissions from traditional air conditioning systems. A major advantage of using climate control instead of AC is that it reduces the amount of electricity used by more than half (typically between 50-70%) which means less power consumption overall, meaning lower costs at home too!
Climate management systems work best in areas where summer temperatures fluctuate widely or there’s a lot of sun exposure during certain times throughout the day (for example near windows). These types can be set up with manual operation modes so they won’t run continuously if you’re not around; Most new models even come equipped with sensors that detect when people enter and leave rooms so it adjusts automatically based on occupancy levels.
Conclusions

Once you know what climate control means, how do we use it? Let’s take a look at some examples…
You walk into your home after work and notice that the temperature inside feels too cold (or hot) so you turn up (or down) the thermostat setting on your HVAC system.
You notice that there’s a lot of dust in the air and decide to run an air purification system with ozone for 30 minutes before going to bed tonight; this will help clear out those nasty allergens while you sleep soundly through it all!
Your family just got back from vacationing outside on hot summer days; now they want their house nice and cool inside so they set up a fan blowing directly at them while sitting around watching movies together as if nothing else mattered in life besides feeling comfy cozy again after being uncomfortable during their trip away from home where no one could regulate climate control variables like temperature or humidity levels properly because they were on vacation!
There are many ways to use climate control to make our lives more comfortable, and it’s important to be aware of all of them so we can choose the best solution for each situation! Stay tuned for more posts about climate control where we will explore these different methods further in detail.
